Positive Displacement Blowers
M-D Pneumatics® blowers and blower packages are known for reliability and quality. Product series offer a range of models and a mix of standard and optional features to a variety of applications. Custom positive displacement (PD) blower packages to 9,000 CFM are available.
New Equipment Request
Please call, email us at info@nwflowtech.com or complete our form if you are looking to purchase new equipment and/or need engineering assistance in designing and building a custom package to meet your application requirements and we’d be happy to send you a quote.
What is a rotary positive displacement blower and how does it work?
Rotary positive displacement blowers, a.k.a. PD blowers, are a constant volume device that employ lobe impellers (often times referred to as rotors) rotating in opposite directions within a blower housing closed at the ends by end plates and traps a certain volume of air or gas then discharges or forces it out against the system pressure.
Gas flows from high pressure to low pressure. Blowers create differential pressure so they can be used to transport air or gas from one location to another. The discharge pressure of the blower needs to be higher than the system pressure if flow is to be established.
Intermeshing lobe impellers mounted on parallel shafts rotate in opposite directions but at the same speed. One lobe impeller is called the driving rotor because it is connected by an external power source such as an AC motor while the opposite lobe impeller is called a driven rotor because it is driven by timing gears connected to the driving rotor. As each lobe impeller passes the blower inlet, it traps a finite volume of air or gas and carries it around the base to the blower outlet where the air is discharged. With constant speed operation, the displaced volume is essentially the same (“positive displacement”) within the blower regardless of pressure, temperature or barometric pressure. There is no change in the volume of the air within the blower but it simply displaces the air or gas from the suction end to the discharge end, against the discharge system resistance (i.e. no compression takes place internal to the blower) in order to move materials in a pipe or hose. Timing gears control the relative position of the rotary lobes to each other and maintain small but finite clearances. This allows operation without lubrication being required inside the lobe cavity.
The illustration below shows the air movement within the blower. The blower can operate in either direction.
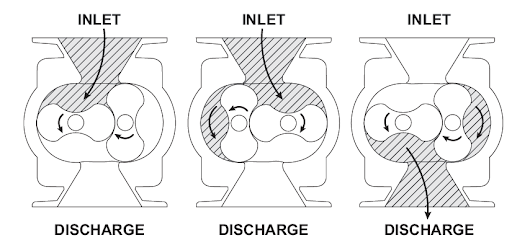
A positive displacement blower pumping capacity is determined by size, operating speed and differential pressure conditions.
Positive displacement blowers have the following characteristics:
- The volumetric flow is primarily dependent on the operating speed.
- The input power is primarily dependent on the total pressure across the blower.
- The suction and discharge pressures are determined by the system conditions.
- The temperature rise of the discharge air is primarily dependent on the differential pressure across the blower.
Example list of common PD Blower Applications by Industry
Here is a list of some of the common industries and applications that utilize positive displacement blowers:
- Aquaculture – Aeration
- Carpet Cleaning – Vacuum Cleaning
- Cement & Lime – Fluidizing, Pneumatic Conveying
- Chemical – Fluidizing, Pneumatic Conveying, Gas Transfer & Boosting, Dust Collection, Vapor Recovery
- Food & Beverage – Pneumatic Conveying, Fluidizing, Dust Collection, Diary Milking, Packaging & Handling
- Oil & Gas – Gas Collection, Vapor Recovery, Steam Compression
- Plastics – Pneumatic Conveying, Dust Collection
- Power & Energy – Pneumatic Conveying, Fluidizing, Gas Transfer, Vapor Recovery, Steam Compression
- Soil Remediation – Vacuum Extraction
- Water & Wastewater Treatment – Aeration






